NA: After Climate Summit Breakthrough: Exploring the Perks of Mini-Nuclear Power Plants
It was quite a spectacle at the recent climate conference in Dubai: 22 nations, including the USA, France, UK, Japan, Belgium, Finland, Sweden, Poland, and Ukraine, formed a global nuclear alliance. Their goal? To triple the worldwide use of nuclear energy by 2050. Why? Because, as a low-emission energy source, nuclear power doesn't contribute to CO2 emissions and thus, global warming. Interestingly, Germany wasn't present at the Dubai Pact.
France's Big Plans: 14 New Reactors
France, fueled by the ambition to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, plans to construct 14 new reactors by 2035. The first six are expected to deliver electricity as early as 2035, with an investment of €1 billion earmarked for researching and developing mini-nuclear power plants.
In the USA, renowned tech entrepreneurs like Bill Gates with TerraPower and Westinghouse, headquartered in Pennsylvania, have championed the use of mini-nuclear power plants as a tool against climate change.
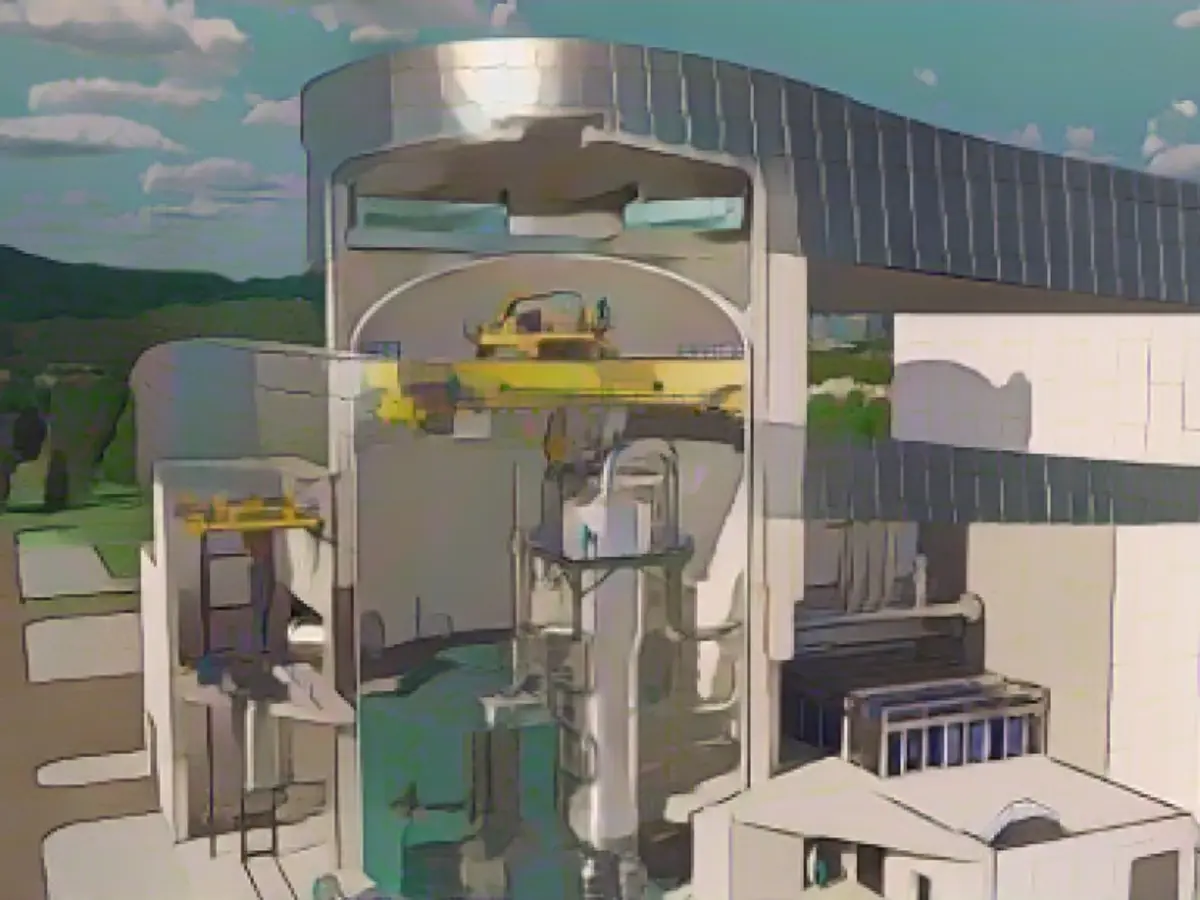
What are Mini-Nuclear Power Plants?
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are prefabricated mini-nuclear power plants designed to deliver up to 300 megawatts, making them smaller than their conventional counterparts. They're manufactured in factories and shipped to their designated locations, offering greater flexibility and customization.
The Size of Mini-Nuclear Power Plants
SMRs with an output of up to 300 megawatts are considered "small," while those with an output between 300 and 700 megawatts are considered "medium." For instance, a modern large nuclear energy plant generates about 1400 megawatts. To put things into perspective, a single MW can provide energy to around 4000 households - a mini-nuclear power plant, such as a 50 MW plant, could be enough for a city like Rostock.
Applications of Mini-Nuclear Power Plants
These mini-nuclear power plants can serve various purposes, including: - supporting energy supply in remote areas with weak grid coverage - providing energy for industries that can benefit from decentralized power sources - replacing coal-fired power plants - functioning as emergency power sources
Safety Measures for Mini-Nuclear Power Plants
SMRs have specific safety advantages, including less radioactive inventory crowded in compared to traditional nuclear power plants.
Cost of Mini-Nuclear Power Plants
The construction cost of a mini-nuclear power plant is estimated to be at least one billion dollars. In the USA, however, the construction of the first planned mini-reactor in November was suspended due to escalating construction costs from $5.3 billion to $9.3 billion.
Curious about nuclear power? Take our survey here: "What are your thoughts on nuclear power plants?"
Nuclear Waste Management
For now, nuclear waste is transported to reprocessing plants where uranium and plutonium are recovered before being stored in containers in interim or final storage facilities. Some countries like Finland and Sweden have built repositories within granite rock.
Visions of a Sustainable Future: Naarea Mini-Nuclear Power Plant in Progress
France-based startup Naarea is currently developing a mini-nuclear power plant, generating 40 megawatts of energy from nuclear waste. Series production is planned to begin in 2030.
Are Mini-Nuclear Power Plants Already in Operation?
According to the World Nuclear Association (WNA), five mini-nuclear power plants are currently in operation in India, Pakistan, and Russia, with an additional four under construction in Argentina, China, and Russia.
Discover whether this photo represents a wolf, a fox, or a cat in our popular article:
While the concept of mini-nuclear power plants offers exciting prospects as a low-emission energy source, addressing challenges pertaining to high capital costs, transportation complexities, regulatory hurdles, and proliferation risks is crucial for their widespread adoption.








