Unveiling the Sun's Gaping Hole and its Impact
An uncommon turn of events unfolded when a recent solar eruption resulted in a colossal hole, or sunspot, on our sun. While sunspots are not an uncommon sight, the latest one had a notable effect: due to the sun's rotation, the dark expanse faced directly towards Earth on December 2. This alignment triggered a powerful solar storm that barreled towards our planet, resulting in significant impact on December 4-5.
According to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the solar storm itself was not excessively strong, maxing out at a level G1 to G2. Nevertheless, the orientation of the eruption towards Earth magnified the effects.
Regularly, the NOAA scrutinizes the prevailing "space weather" and forecasts future solar activity. Additionally, they report on potential solar storm impacts on Earth.
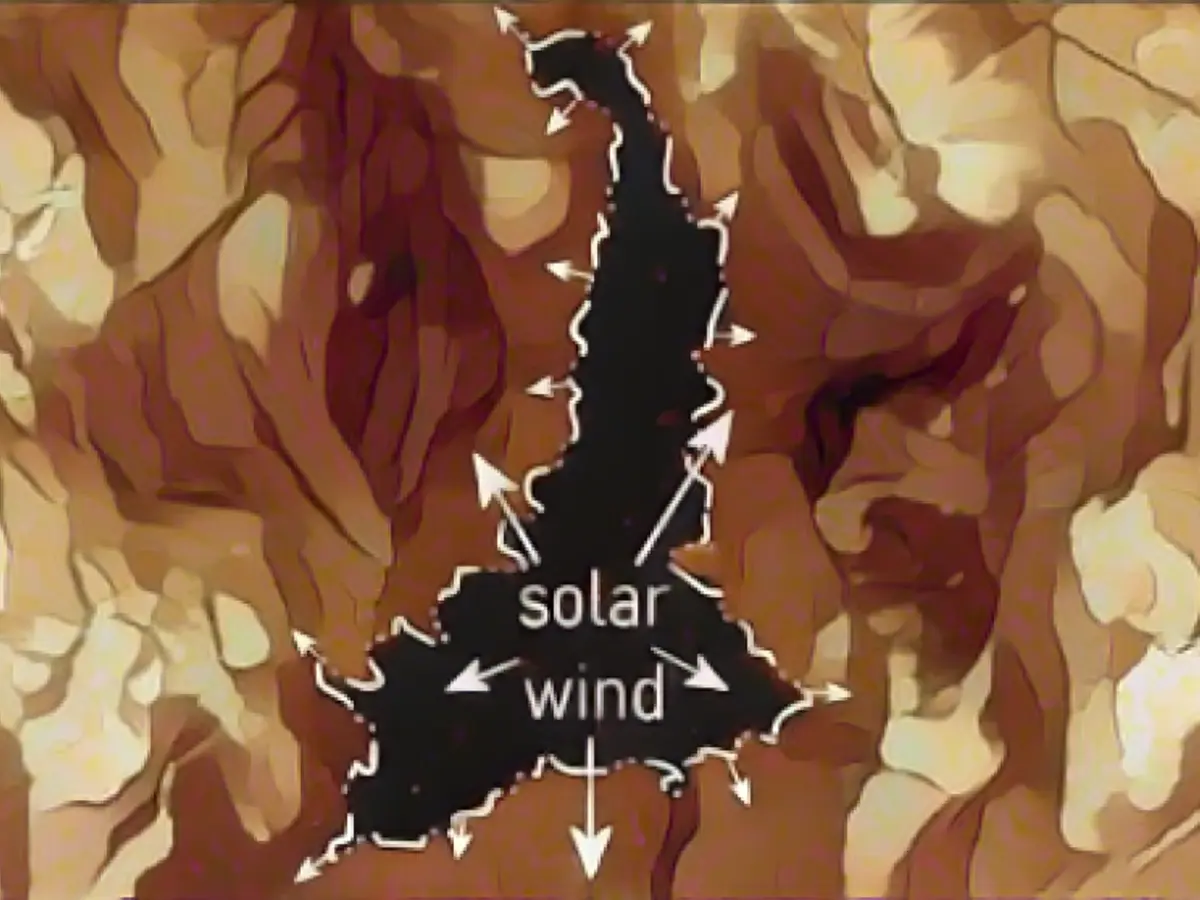
Frequency of such solar eruptions depends on the sun's cycle. These sunspot cycles have an average period of 11.1 years. The NOAA hasn't anticipated any particularly strong activity during the current cycle, with an estimated 173 sunspots (solar eruptions). The mean number is 179 sunspots.
Recently, numerous viewers in non-traditional locations have been marveling at the mesmerizing aurora displays in the sky. In November, an aurora borealis graced Uelzen in Lower Saxony, as well as regions in Bavaria, Hesse, and Saxony.
Consequences of Solar Storms
Solar storms are closely monitored because they can pose potential risks. Among these hazards are severe disruptions to satellite systems, radios, and power grids. Under extreme conditions, satellites that monitor Earth's communication can even fail completely.
More to Explore
- While the NOAA deemed the solar storm as only a G1 to G2 level in strength, the straight-on trajectory towards Earth caused a striking aurora display in formerly uncommon locales, such as Schillig, Lower Saxony.
- A scientist from the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) noted that solar eruptions, like the one responsible for the recent solar storm, are common events on the sun. However, their effects on Earth can differ significantly depending on their orientation and the sun's magnetic field interaction with Earth's.
- Regular monitoring and predicting solar activity, including sunspots and the ensuing solar storms they may cause, plays a crucial role in safeguarding Earth's communication systems, navigation tools, and power lines. During a powerful solar storm, for instance, satellite operations might cease due to communication failures.








